ALOCASIA HARARGANJENSIS
ORIGINAL DESCRIPTION:
Alocasia hararganjensis H. Ara & M.A. Hassan is closely related to Alocasia fallax Schott but readily differentiated by the leaf shape which are narrowly to ovate sagittate with acute tip; tip of the cataphylls c. 8 cm long; and no sterile male zone above the sterile interstice.
Holotype: Bangladesh, Moulvibazar district, Gazipur beat, Hararganj reserve forest, 21.05.2005, Hosne Ara HA 1740 (DACB).
Three new species of Araceae from Bangladesh | Bangladesh Journal of Plant Taxonomy 25(2):227-239
SYNONYMS: N/A
DISTRIBUTION: Bangladesh (NE parts, Habiganj and Moulvibazar districts)
CLIMATE: Tropical humid climate
Humidity is moderate throughout the year, ranging from 60% to 70%
Temperature is varies between the seasons - within the range of 48°F/9°C to 88°F/31°C during the day. Minimum temperatures never dip below 45°F/7°C
Rainy and humid season (October to May) and a dry season between June and October. The average annual rainfall is 1,200 mm
ECOLOGY: Grows on the hill slopes as undergrowth
SPECIES DESCRIPTION:
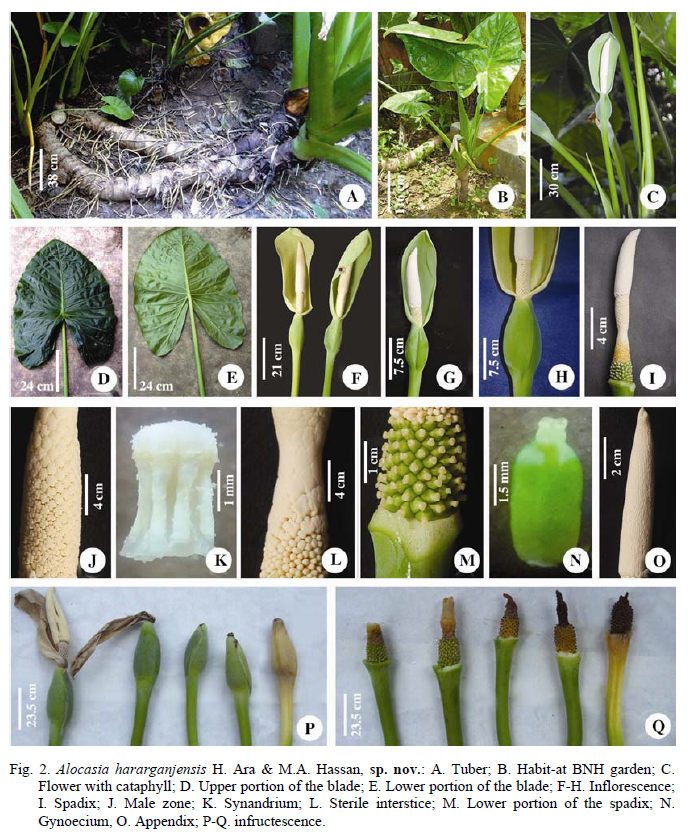
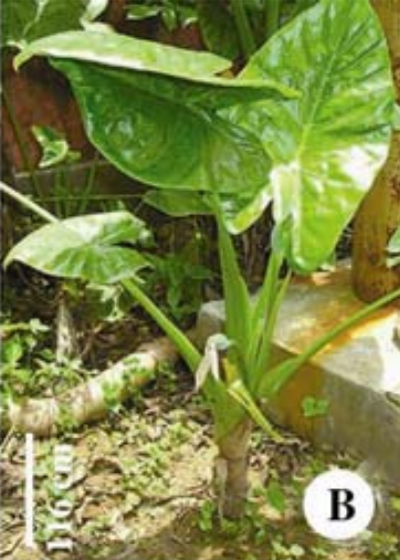
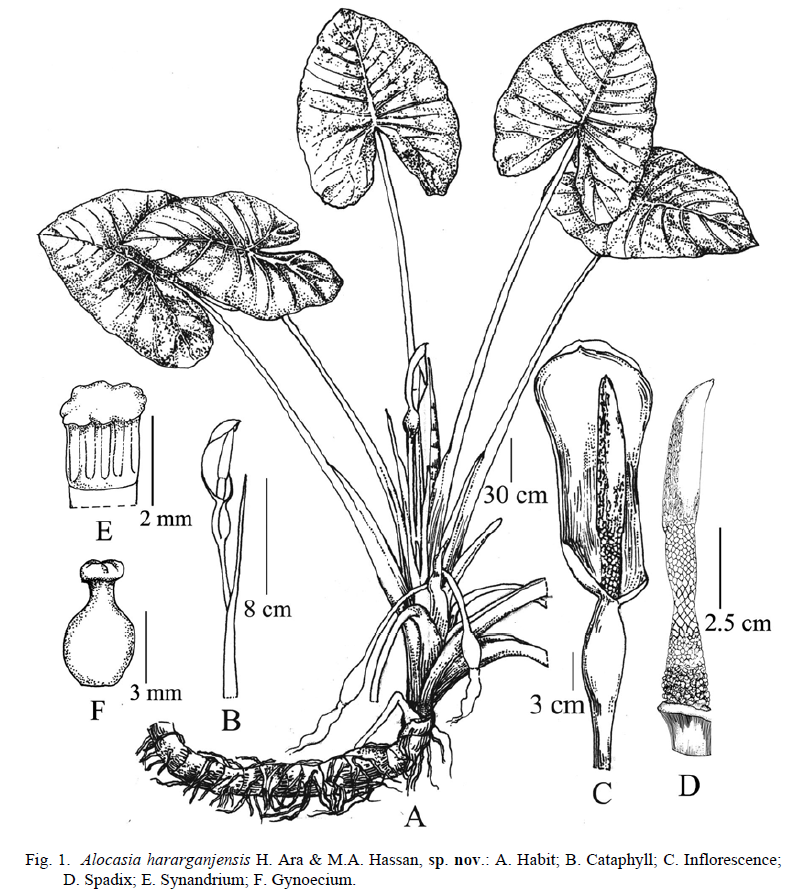
Massive sub-arborescent pachycaul herb, c 3.5 m high. Stem erect to decumbent, c. 10 cm in diameter, c 2.3 m long, clothed in the brown remains of old leaf bases. Leaves several together in terminal crown, held almost erect or slightly curved; petiole c. 1.2 m long, sheathing c. 1/2 from the base of petiole, eglandular, light green, wing of sheath out-rolled; blade narrowly sagittate to ovate-sagittate, slightly glossy, leathery, glabrous, dark-green adaxially, pale green abaxially, usually bullate, 40-50 cm long, base 40-48 cm in diameter, margin entire to slightly sinuate; anterior lobes 35-42 cm long with apiculate tip c. 1 cm long; anterior costa prominent on both surfaces, glabrous, primary veins 7-11 on each side, prominent on both surfaces, diverging at 450- 700; secondary veins flush on both surfaces; interprimary collective veins well-defined; submarginal vein c. 3 mm from the margin; glands in the axils of primary veins absent or extremely inconspicuous; posterior lobes 30-35 cm long, rounded, peltate, c. 1.9 cm long; posterior costae straight
INFLORESCENCE:
Flowering period: March to October
Inflorescences 10 in the centre of the leafy crown, bloom one after another, subtended by cataphylls; cataphylls 66-68 cm long, tip of the cataphylls pointed, c. 8 cm long, green; peduncle smooth, 50-64 cm long, 1.0-1.5 cm in diameter at the base, green. Spathe 18.5-21.0 cm long, constricted at level of sterile zone of spadix; lower spathe 4.5-5.0 cm long, light green, broadly ovoid-cylindric; limb 14-16 cm long, 6.5-7.0 cm in diameter, light greenish yellow, thinly leathery. Spadix shorter than spathe, 12-15 cm long, sessile. Female zone 1.8-2.0 cm long, 1.5-2.0 cm in diameter at the base, with 120-200 close-packed pistils; ovary green, ovoid to subglobose, 2-3 x 2.0-2.3 mm, unilocular, with basal placenta; style 0.5-0.8 mm long, 0.6 mm in diameter, cream coloured; stigma subglobose, shallowly 3-4 lobed, the lobes rounded, creamy; sterile interstice 2.0-2.5 cm long, with 7-8 whorls of rhombohexagonal synandrodia, the lowermost whorls isodiametric with female zone and resembling connate staminodes; sterile male zone absent above the sterile interstice; male zone creamy, 2.5-3.5 cm long, 1.0-1.5 cm in diameter; synandria creamy, rhombo-hexagonal, 2.0-2.3 mm in diameter, opening through apical slits; appendix ivory, 5.5-7.5 cm long, slightly thicker than the male zone at the base, then tapering gradually to a fine point, smooth to faintly rugose. Fruits yellowish (usually does not mature), rather small, 3-4 mm in diameter; fruiting peduncles 40-59 cm long, bend, fruiting spathe whitish, pendulous, 5-6 cm long, the spathe dehiscing longitudinally.
VARIEGATED FORMS: N/A
ETYMOLOGY: The species is named after the type locality-Hararganj in Moulvibazar district in NE Bangladesh, from where the species was first collected.
NOTES:
Conservation status: Near threatened (IUCN, 2017). Restricted distribution. Both in situ and ex situ conservation measures are suggested.
The chromosome number for Alocasia hararganjensis has been determinedappears to be 30. The major morphological differences between Alocasia hararganjensis and its closely allied species Alocasia fallax are outlined below:
Specimens examined: Habiganj: Kalenga beat, Kalenga, 03.07.2005, Hosne Ara HA 1771 (DACB); Moulvibazar: Gazipur beat, Hararganj reserve forest, 07.05.2003, Hosne Ara HA 315 (DACB); Sreemongal, Lawachara reserve forest, 15.05.2005, Hosne Ara HA 1468 (DACB); Madhabkundo, 20.05.2005, Hosne Ara HA 1707 (DACB); Gazipur beat, Hararganj reserve forest, 21.05.2005, Hosne Ara HA 1740 (DACB); Lawachara reserve forest, 04.07.2005, Hosne Ara HA 1779 (DACB); Gazipur beat, Hararganj forest, 05.07.2005, Hosne Ara HA 1804 (DACB); Dhaka: Bangladesh National Herbarium garden (Cultivated), 22.06.2015, Hosne Ara HA 2885 (DACB) [Originally collected from Hararganj reserve forest under Moulvibazar district].
CULTIVARS: N/A
HYBRIDS: N/A